Description
On a N N grid, we place some 1 1 * 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of grid cell (i, j).
Now we view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes.
A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3 dimensional figure to a 2 dimensional plane.
Here, we are viewing the “shadow” when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return the total area of all three projections.
题目链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/projection-area-of-3d-shapes/description/
Difficulty: easy
Example 1:
Input: [[2]]
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 17
Explanation:
Here are the three projections ("shadows") of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
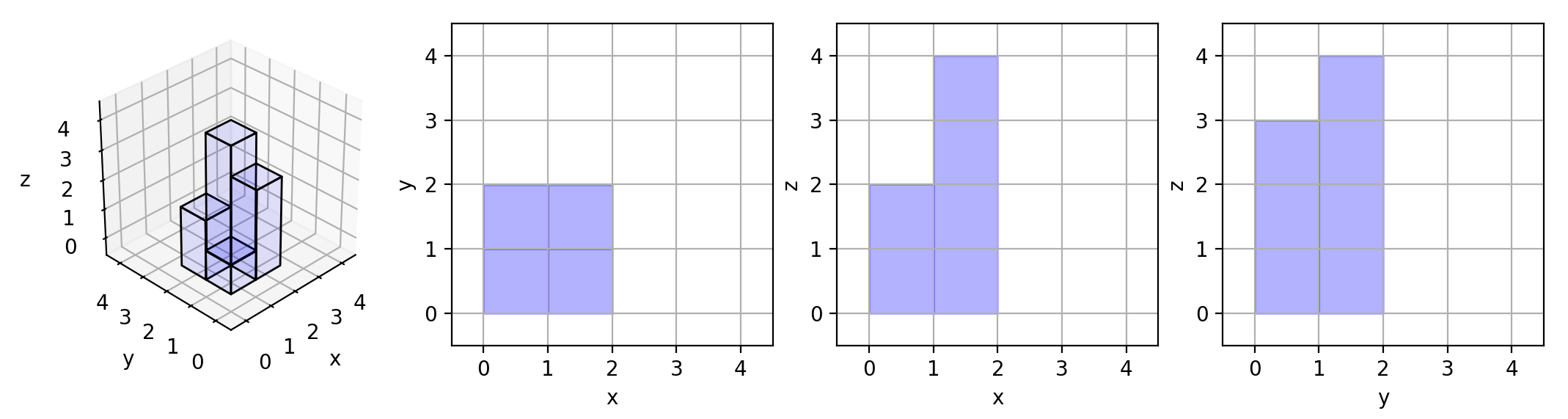
Example 3:
Input: [[1,0],[0,2]]
Output: 8
Example 4:
Input: [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: 14
Example 5:
Input: [[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]]
Output: 21
Note:
- 1 <= grid.length = grid[0].length <= 50
- 0 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
分析
- updating
参考代码
class Solution:
def projectionArea(self, grid):
row=len(grid)
col=len(grid[0])
index=0
for i in range(row):
index+=max(grid[i])
for j in range(col):
ii=0
for i in range(row):
if(grid[i][j]!=0):
index+=1
ii=max(ii,grid[i][j])
index+=ii
return index